Context
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has issued a warning to the Maldives, stressing the urgent need for stronger fiscal consolidation to address the nation's rising economic challenges. The country faces a growing fiscal deficit and increasing reliance on external borrowing, making financial stability a key concern for policymakers.
About the Maldives
Geographical Location & Features
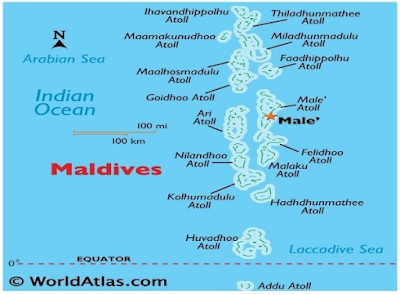
- Location: The Maldives is an island nation located in the Indian Ocean, southwest of Sri Lanka and India, approximately 750 km from the Asian mainland.
- Capital: The capital city, Malé, is the political, economic, and cultural hub of the Maldives. Historically known as the "King’s Island", it has played a central role in governance.
- Composition: The Maldives consists of 1,190 coral islands grouped into 26 atolls arranged in a double chain.
- Unique Island: Addu Atoll is the only Maldivian atoll that extends south of the equator, making it geographically distinct from the rest of the country.
- Natural Channels: The islands are separated by oceanic channels, locally termed “Kandu”, which facilitate marine biodiversity and oceanic flow.
- Topography: The Maldives is one of the flattest countries in the world, with no rivers or mountains. Some islands, like Hithadhoo (Addu Atoll), feature small sand dunes.
Economic Challenges & IMF Warning
The Maldives’ economy is heavily dependent on tourism, contributing to over 30% of its GDP. However, the IMF has raised concerns about:
- Rising National Debt: High borrowing for infrastructure projects has led to fiscal imbalances.
- Budget Deficit: Increased government spending without sufficient revenue generation is widening the fiscal gap.
- Tourism Dependence: A slowdown in global travel due to geopolitical tensions and climate change could significantly impact revenue.
- Need for Fiscal Consolidation: The Maldives must diversify its economy, reduce reliance on external borrowing, and implement stronger financial regulations to ensure long-term sustainability.
Strategic Importance & India's Relations with the Maldives
India-Maldives Military Exercises
India and the Maldives engage in multiple defense collaborations to ensure regional maritime security:
- Exercise Ekuverin – Bilateral military training exercise to strengthen defense cooperation.
- Exercise Dosti – A trilateral coast guard exercise involving India, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka for maritime security.
- Exercise Ekatha – Focuses on anti-piracy and counter-terrorism operations.
- Operation Shield – A security partnership aimed at disaster response and humanitarian assistance.
Geopolitical Importance
- The Maldives’ location in the Indian Ocean makes it crucial for regional trade routes and maritime security.
- India and China are competing for strategic influence in the region, with India supporting infrastructure projects and defense partnerships.
Cultural & Linguistic Aspects
- Official Language: Dhivehi is the national language, spoken exclusively by the Maldivian people.
- Equatorial Presence: The Equator passes through the Maldives, with Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north and Addu Atoll in the south marking the country’s boundaries.
Way Forward for the Maldives
- Economic Diversification – Reducing dependency on tourism and investing in fisheries, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure.
- Debt Management – Implementing strict fiscal policies to control borrowing and ensure sustainable economic growth.
- Maritime Security Partnerships – Strengthening defense collaborations with regional allies like India, Sri Lanka, and the US.
- Climate Adaptation – Developing policies to tackle rising sea levels, which pose an existential threat to the Maldives.
- Investment in Infrastructure – Promoting sustainable development projects to boost economic growth without environmental degradation.
Conclusion
The Maldives faces economic and geopolitical challenges, but strategic reforms in fiscal management, economic diversification, and regional cooperation can ensure long-term stability. Strengthening partnerships with India and other global players will be crucial in maintaining economic resilience and security in the Indian Ocean region.
MCQs for UPSC CSE
Q1: What is the primary economic sector of the Maldives?
a) Agriculture
b) Fisheries
c) Tourism
d) Manufacturing
Answer: c) Tourism
Q2: The Maldives shares maritime borders with which of the following countries?
- India
- Sri Lanka
- Bangladesh
- China
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4
d) 1, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Q3: Which military exercise is a trilateral maritime security cooperation involving India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives?
a) Exercise Ekuverin
b) Exercise Dosti
c) Exercise Ekatha
d) Operation Shield
Answer: b) Exercise Dosti
Q4: Which Maldivian atoll extends south of the Equator?
a) Ihavandhippolhu Atoll
b) Thiladhunmathi Atoll
c) Addu Atoll
d) Malé Atoll
Answer: c) Addu Atoll
Q5: Which international organization recently issued an economic warning to the Maldives?
a) World Bank
b) International Monetary Fund (IMF)
c) United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
d) Asian Development Bank (ADB)
Answer: b) International Monetary Fund (IMF)


.webp)

.webp)



